The probability distribution function of a random variable X is given by
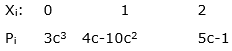
where c > 0
Find:
i. c ii. P(X<2)
iii. P(1<X≤2)
The key point to solve the problem:
If a probability distribution is given then as per its definition, Sum of probabilities associated with each value of a random variable of given distribution is equal to 1
i.e. ∑(pi) = 1
Given probability distribution is:
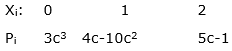
For the probability distribution:
∑(pi) = 1
∴ ![]()
![]()
![]()
Note: It’s better to apply hit and trial method for solving cubic equation, just by putting 1 we get that it satisfies the equation. So ( c - 1 ) will be its one factor. After that divide the polynomial with c-1 which will give a quadratic factor which will be factorized easily.
But we can also proceed as the equation is solved if you can think upto that extent.
![]()
![]()
![]()
(c - 1){3c(c - 2)-1(c - 2)} = 0
(c - 1)(3c - 1)(c - 2) = 0
∴ c = 1 or c = 2 or c = 1/3
As we are given that c > 0
All three values satisfy the given condition, so they must be the values.
BUT BE CAUTIOUS :
As we know that the probability of any event lies between 0 and 1, and we are using c to represent probabilities. So We need to check whether for these values probabilities are defined are valid or not.
Xi : 0 1 2
Pi : 3c3 4c-10c2 5c-1
As this distribution suggests c = 1 and c = 2 are going to make probabilities invalid.
So, c = 1/3 is the only solution for c … (i)
P(X<2) = 1 – P(X = 2)
= 1 – (5c – 1) = 2 – 5c
= 2 – 5/3 = 1/3
P(1 < X ≤ 3) = P(2)
= 5/3 – 1 = 2/3 ……(ii)