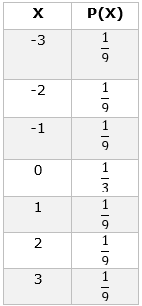
A random variable X takes the values 0, 1, 2 and 3 such that:
P(X = 0) = P(X>0) = P(X<0);
P(X = -3) = P(X = -2) = P(X = -1);
P (X = 1) = P(X = 2) = P(X = 3).
Obtain the probability distribution of X.
The key point to solve the problem:
If a probability distribution is given then as per its definition, Sum of probabilities associated with each value of a random variable of given distribution is equal to 1
i.e. ∑(pi) = 1
Let, P(X = 0) = k
As sum of probabilities associated with each random variable is 1
∴ P(X<0) + P(X = 0) + P(X>0) = 1
k + k + k = 1 {∵ P(X = 0) = P(X>0) = P(X<0)}
3k = 1
∴ k = 1/3
Thus
P(X<0) = 1/3
P(X = -3) + P(X = -2) + P(X = -1) = 1/3
m+m+m = 1/3 {∵ P(X = -3) = P(X = -2) = P(X = -1) = m (say) }
m = 1/9
Similarly,
P(X>0) = 1/3
P (X = 1) + P(X = 2) + P(X = 3) = 1/3
n+n+n = 1/3 {∵ P(X = 3) = P(X = 2) = P(X = 1) = n (say) }
∴ n = 1/9
∴ the required probability distribution is :