The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
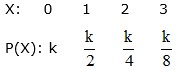
i. Determine the value of k
ii. Determine P (X≤2) and P(X>2)
iii. Find P (X≤2) + P (X>2)
The key point to solve the problem:
If a probability distribution is given then as per its definition, Sum of probabilities associated with each value of a random variable of given distribution is equal to 1
i.e. ∑(pi) = 1
Given distribution is :
(i) 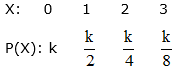
∴ ![]()
![]()
![]()
∴ ![]() (i)
(i)
(ii) P(X>2) = P(X = 3) = ![]()
∴ P(X>2) = ![]()
P(X ≤ 2) = P(X = 0) + P(X = 1) + P(X = 2) = ![]() =
= ![]() …(ii)
…(ii)
(iii) ∴ P(X>2) + P(X≤ 2) = ![]()
29