Let X denote the number of colleges where you will apply after your results and P(X = x) denotes your probability of getting admission in x number of colleges. It is given that
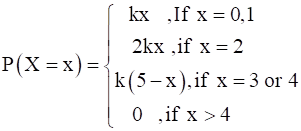
Where k is a positive constant.
Find the value of k. Also, find the probability that you will get admission in (i) exactly one college (ii) at most 2 colleges (iii) at least 2 colleges.
Given,
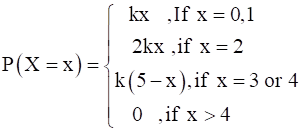
Our variable is X and from equation we see that it is taking values X = 0,1,2,3,4 …… (any whole number)
And it represents the number of colleges in which you are going to get admission.
According to equation given we have :
∴ P(X = 0) = k×0 = 0
P(X = 1) = k×1 = k
P(X = 2) = 2k×2 = 4k
P(X = 3) = k(5-3) = 2k
P(X = 4) = k(5-4) = k
P(X>4) = 0
As in question, it is not given either X is random variable or the given distribution is a probability distribution, we can’t apply any thing directly.
But we have a hint in the question,
As P(X = 0) = 0
It means the chance of not getting admission in any college 0
∴ admission is sure
Hence the sum of all probabilities must be equal to 1 as getting admission has become a sure event.
This makes the given distribution a probability distribution an X a random variable also.
∴ k + 4k+2k+k = 1
8k = 1
k = 1/8
i) P(getting admission in exactly one college) = P(1) = k = 1/8
ii) P(getting admission in atmost 2 colleges) = P(X≤2)
= P(X = 1)+P(X = 2)
= k+4k = 5k = 5/8
iii) P(getting admission in atleast 2 colleges) = P(X≥2)
= P(X = 2)+P(X = 3)+P(X = 4)
= 4k+2k+k = 7k = 7/8