What will happen if a student while studying the dependence of current on the potential difference keeps the circuit closed for a long time to measure the current and potential difference?
According to the Ohm’s law, the potential difference (V) across the ends of a resistor is directly proportional to the current (I) through it provided its temperature remains the same. That is
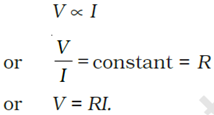
Here R is a constant for the given resistor at a given temperature and is called its resistance. The SI unit of resistance is ohm (W). A graph between the potential difference across the two ends of a resistor and the current through it is a straight line passing through the origin. The slope of this graph gives the resistance R of the resistor. To verify the Ohm’s law, we measure the potential difference across the two ends of a resistor at different currents through it in an electric circuit. The current through the resistor is measured by connecting an ammeter in series with it. The potential difference across the two ends of the resistor is measured by connecting the voltmeter in parallel with it.
Hence, If a student while studying the dependence of current on the potential difference keeps the circuit closed for a long time to measure the current and potential difference, then:
(a) Ammeter’s zero error will change
(b) Ammeter’s will give more reading
(c) A voltmeter will show constantly higher readings
(d) The resistor will get heated up, and its value will change
As the current flows for a long time, the resistor will get heated up, and its value will change as resistance depends on temperature.