If f(1) = 1, f’(1) = 2, then write the value of 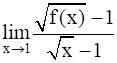
By definition of derivative we know that derivative of a function at a given real number say c is given by :
f’(c) = ![]()
let Z = ![]()
As Z is taking 0/0 form because f(1) = 1
So on rationalizing the Z, we have–
Z = ![]()
⇒ Z = 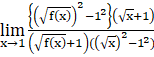 {using a2–b2 = (a+b)(a–b)}
{using a2–b2 = (a+b)(a–b)}
⇒ Z = ![]()
Using algebra of limits, we have –
Z = ![]()
Using the definition of the derivative, we have –
Z = ![]()
⇒ Z = 2 × (2/2) = 2 {using values given in equation}
∴ Z = 2
11