Prove that the straight lines (a + b)x + (a – b)y = 2ab, (a – b)x + (a + b)y = 2ab and x + y = 0 form an isosceles triangle whose vertical angle is 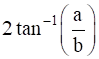 .
.
Given:
The given lines are
(a + b) x + (a − b) y = 2ab … (1)
(a − b) x + (a + b) y = 2ab … (2)
x + y = 0 … (3)
To prove:
The straight lines (a + b)x + (a – b)y = 2ab, (a – b)x + (a + b)y = 2ab and x + y = 0 form an isosceles triangle whose vertical angle is ![]()
Assuming:
Let m1, m2 and m3 be the slopes of the lines (1), (2) and (3), respectively.
Explanation:
Now,
Slope of the first line = m1 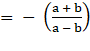
Slope of the second line = m2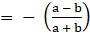
Slope of the third line = m3 = -1
Let θ1 be the angle between lines (1) and (2), θ2 be the angle between lines (2) and (3) and θ3 be the angle between lines (1) and (3).
∴ 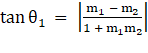

⇒ 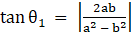
⇒ 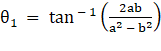
∴ 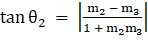
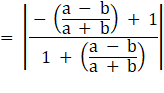
⇒ 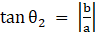
⇒ 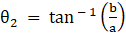
∴ 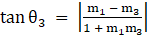
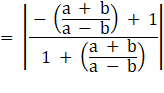
⇒ 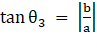
⇒ 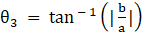
Here,
θ2 = θ3 and ![]()
Hence proved, the given lines form an isosceles triangle whose vertical angle is ![]()