Show that the path of a moving point such that its distances from two lines 3x – 2y = 5 and 3x + 2y = 5 are equal is a straight line.
Given:
Two lines 3x – 2y = 5 and 3x + 2y = 5
To prove:
The path of a moving point such that its distances from two lines 3x – 2y = 5 and 3x + 2y = 5 are equal is a straight line
Concept Used:
Distance of a point from a line.
Explanation:
Let P(h, k) be the moving point such that it is equidistant from the lines 3x − 2y = 5 and 3x + 2y = 5
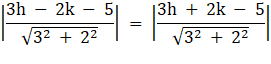
⇒ |3h – 2k – 5| = |3h + 2k – 5|
⇒ 3h – 2k – 5 = ±(3h + 2k – 5)
⇒ 3h – 2k – 5 = 3h + 2k – 5 and 3h – 2k – 5 = -3h + 2k – 5
⇒ k = 0 and 3h = 5
Hence proved, the path of the moving points are 3x = 5 or y = 0. These are straight lines.
13