Let A = R – {3}, B = R – {1}. Let f : A → B be defined by 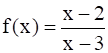 ∀ x ∈ A . Then show that f is bijective.
∀ x ∈ A . Then show that f is bijective.
Given that, ![]()
In order to prove that f is one-one, it is sufficient to prove that f(x1)=f(x2) ⇒ x1=x2∀ x1, x2 ∈ A .
Let f(x1)=f(x2)
⇒ ![]()
⇒ (x1-2)(x2-3) = (x2-2)(x1-3)
⇒ x1x2-3x1-2x2+6 = x1x2-3x2-2x1+6
⇒ -3x1-2x2 = -3x2-2x1
⇒ -3x1+2x1 = -3x2+2x2
⇒ (-3+2) x1 = (-3+2)x2
⇒ x1 = x2
∴ f is one-one.
f is onto if every element of B is the f-image of some element of A.
let f(x) = y
⇒ ![]()
⇒ x-2 = y(x-3)
⇒ x-2 = xy-3y
⇒ x-xy = -3y+2
⇒ x(1-y) = -3y+2
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
Thus, for each y ∈ B there exists ![]() such that f(x) = y.
such that f(x) = y.
Hence, f is onto.
Since, f is one-one and onto therefore f is bijective.
20