Minimise Z = 13x – 15y subject to the constraints: x + y ≤ 7, 2x – 3y + 6 ≥ 0, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Given:
Z=13x – 15y
It is subject to constraints
x + y ≤ 7, 2x – 3y + 6 ≥ 0, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Now let us convert the given inequalities into equation.
We obtain the following equation
x + y ≤ 7
⇒ x + y=7
2x – 3y + 6 ≥ 0
⇒ 2x-3y+6=0
x ≥ 0
⇒ x=0
y ≥ 0
⇒ y=0
The region represented by x+y≤7:
The line x + y=7 meets the coordinate axes (7,0) and (0,7) respectively. We will join these points to obtain the line x + y=7. It is clear that (0,0) satisfies the inequation x+y≤7. So the region containing the origin represents the solution set of the inequation x+y≤7
The region represented by 2x – 3y + 6 ≥ 0:
The line 2x-3y+6=0 meets the coordinate axes (-3,0) and (0,2) respectively. We will join these points to obtain the line 2x-3y+6=0. It is clear that (0,0) satisfies the inequation 2x – 3y + 6 ≥ 0. So, the region containing the origin represents the solution set of the inequation 2x – 3y + 6 ≥ 0
Region represented by x≥0 and y≥0 is first quadrant, since every point in the first quadrant satisfies these inequations.
Plotting these equations graphically, we get
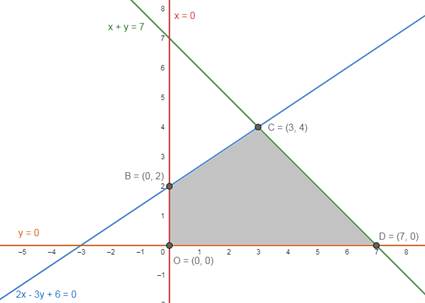
The shaded region OBCD is the feasible region is bounded, so, minimum value will occur at a corner point of the feasible region.
Corner Points are O (0, 0), B (0, 2), C (3, 4) and D (7,0)
Now we will substitute these values in Z at each of these corner points, we get
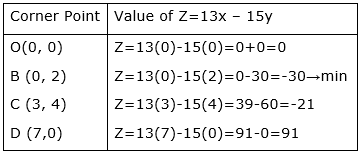
Hence, the minimum value of Z is -30 at the point (0, 2).