A hospital dietician wishes to find the cheapest combination of two foods, A and B, that contains at least 0.5 milligram of thiamine and at least 600 calories. Each unit of A contains 0.12 milligram of thiamine and 100 calories, while each unit of B contains 0.10 milligram of thiamine and 150 calories. If each food costs 10 paise per unit, how many units of each should be combined at a minimum cost?
The above information can be expressed using the following table:
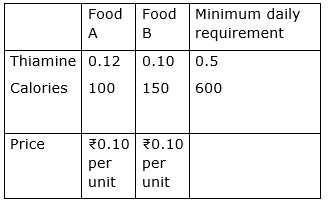
Let the quantity of the foods A and B be ‘x’ and ‘y’ respectively.
Cost of food A = 0.10x
Cost of food B = 0.10y
Cost of diet = 0.10x + 0.10y
Now,
⟹ 0.12x + 0.10y ≥ 0.5
i.e. the minimum requirement of thiamine in the foods is 0.5mg
⟹ 100x + 150y ≥ 600
i.e. the minimum requirement of calories in the foods is 600.
Hence, mathematical formulation of the LPP is as follows:
Find ‘x’ and ‘y’ that:
Minimises Z = 0.10x + 0.10y
Subject to the following constraints:
(i) 0.12x + 0.10y ≥ 0.5
(ii) 100x + 150y ≥ 600
i.e. 2x + 3y ≥ 12
(iii) x,y ≥ 0 (∵ quantity cant be negative)
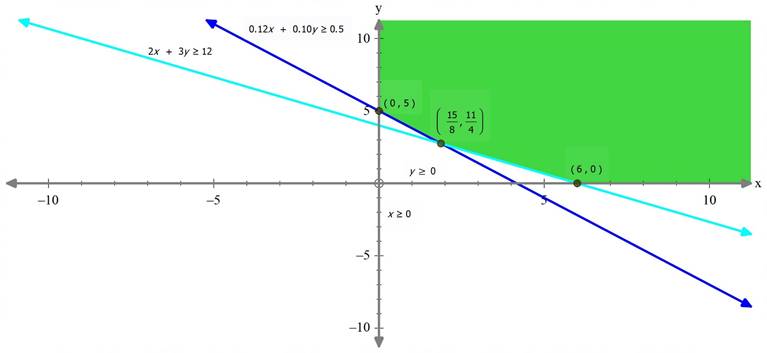
The feasible region is unbounded.
The corner points of the feasible region is as follows:
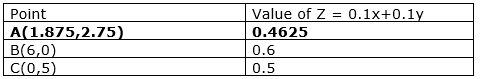
Z is smallest at A(1.875,2.75)
Let us consider 0.1x+0.1y ≤ 0.4625
As it has no intersection with the feasible region, the smallest value is the minimum value.
The minimum cost of the foods is ₹0.4625