For any Δ ABC show that -
a cos A + b cos B + c cos C = 2b sin A sin C
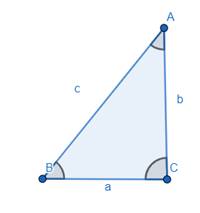
Note: In any ΔABC we define ‘a’ as the length of the side opposite to ∠A, ‘b’ as the length of the side opposite to ∠B and ‘c’ as the length of the side opposite to ∠C.
The key point to solve the problem:
The idea of sine Formula:
• ![]()
As we have to prove:
a cos A + b cos B + c cos C = 2b sin A sin C
We can observe that we all the terms present in the equation to be proved are not showing any resemblance with known formula but the term is RHS side has sine terms, so there is a possibility that sine formula can solve our problem
∴ from sine formula we have-
![]()
∴ a = 2k sin A , b = 2k sin B , c = 2k sin C
As,
LHS = a cos A + b cos B + c cos C
= 2k sin A cos A + 2k sin B cos B + 2k sin C cos C
= k(2sin A cos A + 2sin B cos B + 2sin C cos C
LHS = k( sin 2A + sin 2B + sin 2C) {using 2 sin X cos X = sin 2X }
Using transformation formula – sin X + sin Y = ![]()
LHS = k ( 2sin(A + B) cos (A – B) + sin 2C)
∵ ∠ A + ∠ B + ∠ C = π
∴ A + B = π – C
∴ LHS = k { 2sin (π – C) cos (A – B) + 2 sin C cos C }
[as sin (π – θ) = sin θ]
LHS = k{ 2 sin C cos (A – B) + 2 sin C cos C }
LHS = 2k sin C { cos (A – B) + cos C }
Using transformation formula – cos X + cos Y = ![]()
LHS = 2k sin C { ![]() }
}
LHS = 4k sin C ![]() {∵∠ A + ∠ B + ∠ C = π }
{∵∠ A + ∠ B + ∠ C = π }
LHS = 4k sin C sin B sin A
∵ 2k sin B = b
We have,
LHS = 2b sin A sin C = RHS …..Hence proved.