For any Δ ABC show that –
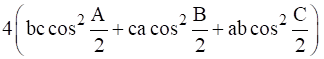 = (a+b+c)2
= (a+b+c)2
Note: In any ΔABC we define ‘a’ as the length of the side opposite to ∠A, ‘b’ as the length of the side opposite to ∠B and ‘c’ as the length of the side opposite to ∠C.
The key point to solve the problem:
The idea of cosine formula in ΔABC
• Cos A = ![]()
• Cos B = ![]()
• Cos C = ![]()
As we have to prove:
![]() = (a+b+c)2
= (a+b+c)2
The form required to prove contains similar terms as present in cosine formula.
∴ Cosine formula is the perfect tool for solving the problem.
As we see the expression has bc, ac and ab terms so we will apply the formula of cos A, cos B, and cos C all.
As cos A = ![]()
⇒ 2bc cos A = b2 + c2 – a2
We need (b + c )2 in our proof so adding 2bc both sides –
∴ 2bc + 2bc cos A = b2 + c2 +2bc – a2
⇒ 2bc ( 1 + cos A) = (b + c)2 - a2
∵ 1 + cos A = 2cos2 (A / 2) { using multiple angle formulae }
∴ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]() ….eqn 1
….eqn 1
Similarly,
![]() ….eqn 2
….eqn 2
And,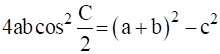 ….eqn 3
….eqn 3
Adding equation 1, 2 and 3 we have –
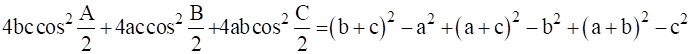
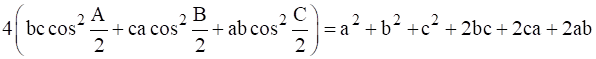
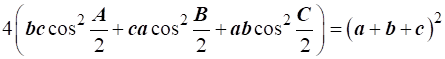 …Hence proved
…Hence proved