(i) A gene can express more than one trait. What gives rise to different expressions?
(ii) When a true breeding pea plant which has yellow seeds is pollinated by a plant that has green seeds, all the F 1 plants have yellow seeds. What might have been the allele for yellow seeds (tell whether it was dominant or recessive / heterozygous or homozygous )?
i) A gene codes for a character which has two or more contrasting traits. If we see in the sweet pea plant taken by Mendel for his experiments on genetics, a single gene codes for the height of the pea plant. It has two different traits governed by two different alleles T and t. The combination of these two alleles codes for the different type of height of the pea plant. TT or Tt codes for tall plant whereas tt codes for the dwarf plant.
ii) To determine the alleles of the yellow seed. To show whether it is homozygous or heterozygous, dominant or recessive.
YY/Yy codes for yellow seeds of the true breeding pea plant
yy codes for green seeds of another pea plant
When a cross is conducted between true breeding pea plant which has yellow seeds and another pea plant which has green seeds and the first generation produced has yellow seeds. The test conducted to determine the allele of the parent plant is known is known as test cross.
Below given are the crosses to check the two possibilities.
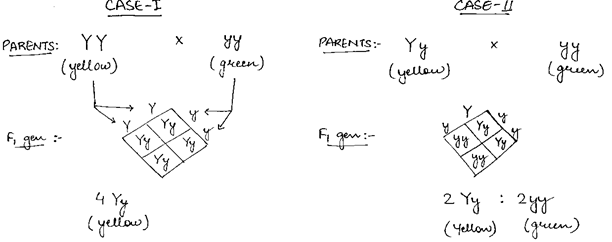
By seeing the cases we can say that the yellow colour of the speed of the pea plant is homozygously dominant i. e. YY.