Table of Contents
 Chapter 5
Chapter 5
Understanding Elementary Shapes
5.1 Introduction
All the shapes we see around us are formed using curves or lines. We can see corners, edges, planes, open curves and closed curves in our surroundings. We organise them into line segments, angles, triangles, polygons and circles. We find that they have different sizes and measures. Let us now try to develop tools to compare their sizes.
5.2 Measuring Line Segments
We have drawn and seen so many line segments. A triangle is made of three, a quadrilateral of four line segments.
A line segment is a fixed portion of a line. This makes it possible to measure a line segment. This measure of each line segment is a unique number called its “length”. We use this idea to compare line segments.
To compare any two line segments, we find a relation between their lengths. This can be done in several ways.
(i) Comparison by observation:
By just looking at them can you tell which one is longer?

You can see that 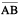 is longer.
is longer.
But you cannot always be sure about your usual judgment.
For example, look at the adjoining segments :

The difference in lengths between these two may not be obvious. This makes other ways of comparing necessary.
In this adjacent figure, 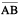 and
and  have the same lengths. This is not quite obvious.
have the same lengths. This is not quite obvious.
So, we need better methods of comparing line segments.
(ii) Comparison by Tracing
To compare 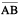 and
and 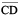 , we use a tracing paper, trace
, we use a tracing paper, trace 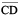 and place the traced segment on
and place the traced segment on 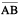 .
.


Can you decide now which one among 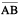 and
and 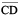 is longer?
is longer?
The method depends upon the accuracy in tracing the line segment. Moreover, if you want to compare with another length, you have to trace another line segment. This is difficult and you cannot trace the lengths everytime you want to compare them.
(iii) Comparison using Ruler and a Divider
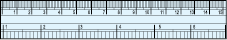
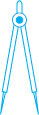
Ruler Divider
Have you seen or can you recognise all the instruments in your instrument box? Among other things, you have a ruler and a divider.
Note how the ruler is marked along one of its edges. It is divided into 15 parts. Each of these 15 parts is of length 1cm.
Each centimetre is divided into 10subparts.
Each subpart of the division of a cm is 1mm.
1 mm is 0.1 cm.
2 mm is 0.2 cm and so on .
2.3 cm will mean 2 cm and 3 mm.
How many millimetres make one centimetre? Since 1cm = 10 mm, how will we write 2 cm? 3mm? What do we mean by 7.7 cm?
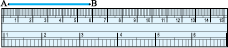
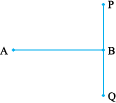
Place the zero mark of the ruler at A. Read the mark against B. This gives the length of  . Suppose the length is 5.8 cm, we may write,
. Suppose the length is 5.8 cm, we may write,
Length AB = 5.8 cm or more simply as AB = 5.8 cm.
There is room for errors even in this procedure. The thickness of the ruler may cause difficulties in reading off the marks on it.
Think, discuss and write
1. What other errors and difficulties might we face?
2. What kind of errors can occur if viewing the mark on the ruler is not proper? How can one avoid it?
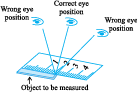
Positioning error
To get correct measure, the eye should be correctly positioned, just vertically above the mark. Otherwise errors can happen due to angular viewing.
Can we avoid this problem? Is there a better way?
Let us use the divider to measure length.
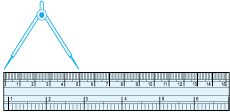
Open the divider. Place the end point of one of its arms at A and the end point of the second arm at B. Taking care that opening of the divider is not disturbed, lift the divider and place it on the ruler. Ensure that one end point is at the zero mark of the ruler. Now read the mark against the other end point.
1. Take any post card. Use the above technique to measure its two adjacent sides.
2. Select any three objects having a flat top. Measure all sides of the top using a divider and a ruler.
Exercise 5.1
1. What is the disadvantage in comparing line segments by mere observation?
2. Why is it better to use a divider than a ruler, while measuring the length of a line segment?
3. Draw any line segment, say AB . Take any point C lying in between A and B. Measure the lengths of AB, BC and AC. Is AB = AC + CB?
[Note : If A,B,C are any three points on a line such that AC + CB = AB, then we can be sure that C lies between A and B.]
4. If A,B,C are three points on a line such that AB = 5 cm, BC = 3 cm and AC = 8 cm, which one of them lies between the other two?
5. Verify, whether D is the mid point of AG .
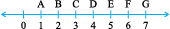
6. If B is the mid point of AC and C is the mid point of BD , where A,B,C,D lie on a straight line, say why AB = CD?
7. Draw five triangles and measure their sides. Check in each case, if the sum of the lengths of any two sides is always less than the third side.
5.3 Angles – ‘Right’ and ‘Straight’
You have heard of directions in Geography. We know that China is to the north of India, Sri Lanka is to the south. We also know that Sun rises in the east and sets in the west. There are four main directions. They are North (N), South (S), East (E) and West (W).
Do you know which direction is opposite to north?
Which direction is opposite to west?
Just recollect what you know already. We now use this knowledge to learn a few properties about angles.
Stand facing north.
Turn clockwise to east.
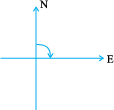
We say, you have turned through a right angle.
Follow this by a ‘right-angle-turn’, clockwise.
You now face south.
If you turn by a right angle in the anti-clockwise direction, which direction will you face? It is east again! (Why?)
Study the following positions :
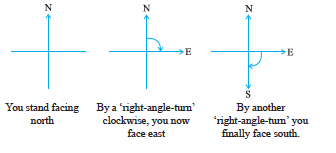
From facing north to facing south, you have turned by two right angles. Is not this the same as a single turn by two right angles?
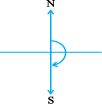
The turn from north to east is by a right angle.
The turn from north to south is by two right angles; it is called a straight angle. (NS is a straight line!)
Stand facing south.

Turn by a straight angle.
Which direction do you face now?
You face north!
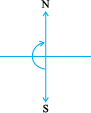
To turn from north to south, you took a straight angle turn, again to turn from south to north, you took another straight angle turn in the same direction. Thus, turning by two straight angles you reach your original position.
Think, discuss and write
By how many right angles should you turn in the same direction to reach your original position?
Turning by two straight angles (or four right angles) in the same direction makes a full turn. This one complete turn is called one revolution. The angle for one revolution is a complete angle.

We can see such revolutions on clock-faces. When the hand of a clock moves from one position to another, it turns through an angle.
Suppose the hand of a clock starts at 12 and goes round until it reaches at 12 again. Has it not made one revolution? So, how many right angles has it moved? Consider these examples :
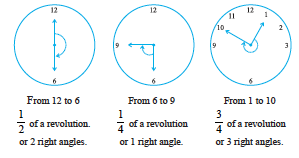
![]()
1. What is the angle name for half a revolution?
2. What is the angle name for one-fourth revolution?
3. Draw five other situations of one-fourth, half and three-fourth revolution on a clock.
Note that there is no special name for three-fourth of a revolution.
Exercise 5.2
1. What fraction of a clockwise revolution does the hour hand of a clock turn through, when it goes from
(a) 3 to 9 (b) 4 to 7 (c) 7 to 10
(d) 12 to 9 (e) 1 to 10 (f) 6 to 3
2. Where will the hand of a clock stop if it
(a) starts at 12 and makes 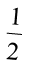 of a revolution, clockwise?
of a revolution, clockwise?
(b) starts at 2 and makes 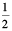 of a revolution, clockwise?
of a revolution, clockwise?
(c) starts at 5 and makes 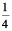 of a revolution, clockwise?
of a revolution, clockwise?
(d) starts at 5 and makes 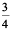 of a revolution, clockwise?
of a revolution, clockwise?
3. Which direction will you face if you start facing
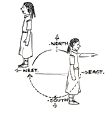
(a) east and make 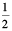 of a revolution clockwise?
of a revolution clockwise?
(b) east and make 1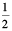 of a revolution clockwise?
of a revolution clockwise?
(c) west and make 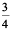 of a revolution anti-clockwise?
of a revolution anti-clockwise?
(d) south and make one full revolution?
(Should we specify clockwise or anti-clockwise for this last question? Why not?)
4. What part of a revolution have you turned through if you stand facing
(a) east and turn clockwise to face north?
(b) south and turn clockwise to face east?
(c) west and turn clockwise to face east?
5. Find the number of right angles turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from
(a) 3 to 6 (b) 2 to 8 (c) 5 to 11
(d) 10 to 1 (e) 12 to 9 (f) 12 to 6
6. How many right angles do you make if you start facing
(a) south and turn clockwise to west?
(b) north and turn anti-clockwise to east?
(c) west and turn to west?
(d) south and turn to north?
7. Where will the hour hand of a clock stop if it starts
(a) from 6 and turns through 1 right angle?
(b) from 8 and turns through 2 right angles?
(c) from 10 and turns through 3 right angles?
(d) from 7 and turns through 2 straight angles?
5.4 Angles – ‘Acute’, ‘Obtuse’ and ‘Reflex’
We saw what we mean by a right angle and a straight angle. However, not all the angles we come across are one of these two kinds. The angle made by a ladder with the wall (or with the floor) is neither a right angle nor a straight angle.
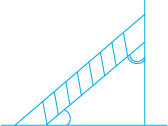
Think, discuss and write
Are there angles smaller than a right angle?
Are there angles greater than a right angle?
Have you seen a carpenter’s square? It looks like the letter “L” of English alphabet. He uses it to check right angles. Let us also make a similar ‘tester’ for a right angle.
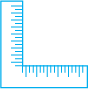
![]()
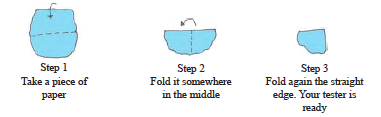
Observe your improvised ‘right-angle-tester’. [Shall we call it RA tester?]
Does one edge end up straight on the other?
Suppose any shape with corners is given. You can use your RA tester to test the angle at the corners.
Do the edges match with the angles of a paper? If yes, it indicates a right angle.
![]()
1. The hour hand of a clock moves from 12 to 5. Is the revolution of the hour hand more than 1 right angle?
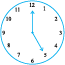
2. What does the angle made by the hour hand of the clock look like when it moves from 5 to 7. Is the angle moved more than 1 right angle?

3. Draw the following and check the angle with your RA tester.
(a) going from 12 to 2 (b) from 6 to 7
(c) from 4 to 8 (d) from 2 to 5
4. Take five different shapes with corners. Name the corners. Examine them with your tester and tabulate your results for each case :
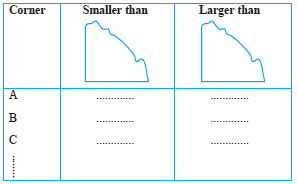
Other names
• An angle smaller than a right angle is called an acute angle. These are acute angles.

Do you see that each one of them is less than one-fourth of a revolution? Examine them with your RA tester.
• If an angle is larger than a right angle, but less than a straight angle, it is called an obtuse angle. These are obtuse angles.


Do you see that each one of them is greater than one-fourth of a revolution but less than halfa revolution? Your RA tester may help to examine.
Identify the obtuse angles in the previous examples too.
• A reflex angle is larger than a straight angle. It looks like this. (See the angle mark)

Were there any reflex angles in the shapes you made earlier?
How would you check for them?
![]()
1. Look around you and identify edges meeting at corners to produce angles. List ten such situations.
2. List ten situations where the angles made are acute.
3. List ten situations where the angles made are right angles.
4. Find five situations where obtuse angles are made.
5. List five other situations where reflex angles may be seen.
Exercise 5.3
1. Match the following :
(i) Straight angle (a) Less than one-fourth of a revolution
(ii) Right angle (b) More than half a revolution
(iii) Acute angle (c) Half of a revolution
(iv) Obtuse angle (d) One-fourth of a revolution
(v) Reflex angle (e) Between 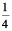 and
and 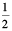 of a revolution
of a revolution
(f) One complete revolution
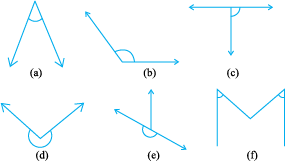
2. Classify each one of the following angles as right, straight, acute, obtuse or reflex :
5.5 Measuring Angles
The improvised ‘Right-angle tester’ we made is helpful to compare angles with a right angle. We were able to classify the angles as acute, obtuse or reflex.
But this does not give a precise comparison. It cannot find which one among the two obtuse angles is greater. So in order to be more precise in comparison, we need to ‘measure’ the angles. We can do it with a ‘protractor’.
The measure of angle
We call our measure, ‘degree measure’. One complete revolution is divided into 360 equal parts. Each part is a degree. We write 360° to say ‘three hundred sixty degrees’.
Think, discuss and write
How many degrees are there in half a revolution? In one right angle? In one straight angle?
How many right angles make 180°? 360°?
![]()
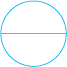
1. Cut out a circular shape using a bangle or take a circular sheet of about the same size.

2. Fold it twice to get a shape as shown. This is called a quadrant.
3. Open it out. You will find a semi-circle with a fold in the middle. Mark 90o on the fold.
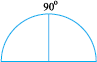
4. Fold the semicircle to reach the quadrant. Now fold the quadrant once more as shown. The angle is half of 90o i.e. 45o.
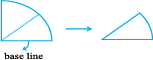
5. Open it out now. Two folds appear on each side. What is the angle upto the first new line? Write 45o on the first fold to the left of the base line.
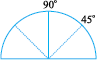
6. The fold on the other side would be 90o + 45o = 135o
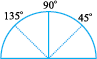
7. Fold the paper again upto 45° (half of the quadrant). Now make half of this. The first fold to the left of the base line now is half of 45° i.e. 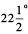 . The angle on the left of 135o would be
. The angle on the left of 135o would be 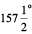 .
.
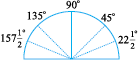
You have got a ready device to measure angles. This is an approximate protractor.
The Protractor
You can find a readymade protractor in your ‘instrument box’. The curved edge is divided into 180 equal parts. Each part is equal to a ‘degree’. The markings start from 0° on the right side and ends with 180° on the left side, and vice-versa.
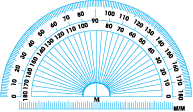
Suppose you want to measure an angle ABC.

Given ∠ABC Measuring ∠ABC
1. Place the protractor so that the mid point (M in the figure) of its straight edge lies on the vertex B of the angle.
2. Adjust the protractor so that BC is along the straight-edge of the protractor.
3. There are two ‘scales’ on the protractor : read that scale which has the 0° mark coinciding with the straight-edge (i.e. with ray BC).
4. The mark shown by BA on the curved edge gives the degree measure of the angle.
We write m∠ABC = 40°, or simply ∠ABC = 40°.
Exercise 5.4
1. What is the measure of (i) a right angle? (ii) a straight angle?
2. Say True or False :
(a) The measure of an acute angle < 90°.
(b) The measure of an obtuse angle < 90°.
(c) The measure of a reflex angle > 180°.
(d) The measure of one complete revolution = 360°.
(e) If m∠A = 53° and m∠B = 35°, then m∠A > m∠B.
3. Write down the measures of
(a) some acute angles. (b) some obtuse angles.
(give at least two examples of each).
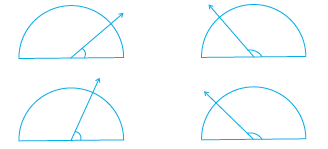
4. Measure the angles given below using the Protractor and write down the measure.
5. Which angle has a large measure?
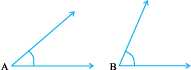
First estimate and then measure.
Measure of Angle A =
Measure of Angle B =
6. From these two angles which has larger measure? Estimate and then confirm by measuring them.

7. Fill in the blanks with acute, obtuse, right or straight :
(a) An angle whosemeasure is less than that of a right angle is______.
(b) An angle whose measure is greater than that of a right angle is ______.
(c) An angle whose measure is the sum of the measures of two right angles is _____.
(d) When the sum of the measures of two angles is that of a right angle, then each one of them is ______.
(e) When the sum of the measures of two angles is that of a straight angle and if one of them is acute then the other should be _______.
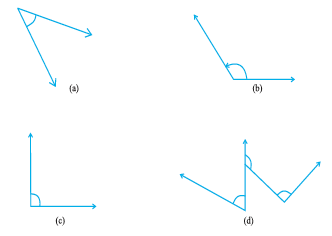
8. Find the measure of the angle shown in each figure. (First estimate with your eyes and then find the actual measure with a protractor).
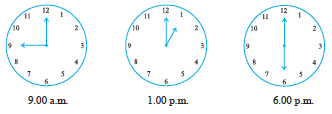
9. Find the angle measure between the hands of the clock in each figure :
In the given figure, the angle measures 30°. Look at the same figure through a magnifying glass. Does the angle becomes larger? Does the size of the angle change?

11. Measure and classify each angle :
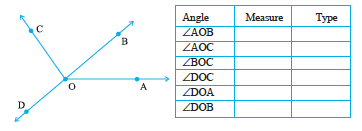
5.6 Perpendicular Lines
When two lines intersect and the angle between them is a right angle, then the lines are said to be perpendicular. If a line AB is perpendicular to CD, we write AB ⊥ CD.
Think, discuss and write
If AB ⊥ CD, then should we say that CD ⊥ AB also?
Perpendiculars around us!
You can give plenty of examples from things around you for perpendicular lines (or line segments). The English alphabet T is one. Is there any other alphabet which illustrates perpendicularity?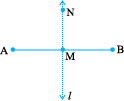
Consider the edges of a post card. Are the edges perpendicular?
Let AB be a line segment. Mark its mid point as M. Let MN be a line perpendicular to AB through M.
Does MN divide AB into two equal parts?
MN bisects AB (that is, divides AB into two equal parts) and is also perpendicular to AB .
So we say MN is the perpendicular bisector of AB .
You will learn to construct it later.
Exercise 5.5
1. Which of the following are models for perpendicular lines :
(a) The adjacent edges of a table top.
(b) The lines of a railway track.
(c) The line segments forming the letter ‘L’.
(d) The letter V.
2. Let PQ be the perpendicular to the line segment XY. Let PQ and XYintersect in the point A. What is the measure of ∠PAY ?
3. There are two set-squares in your box. What are the measures of the angles that are formed at their corners? Do they have any angle measure that is common?
4. Study the diagram. The line l is perpendicular to line m
(a) Is CE = EG?
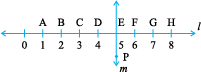
(b) Does PE bisect CG?
(c) Identify any two line segments for which PE is the perpendicular bisector.
(d) Are these true?
(i) AC > FG
(ii) CD = GH
(iii) BC < EH.
5.7 Classification of Triangles
Do you remember a polygon with the least number of sides? That is a triangle. Let us see the different types of triangle we can get.
![]()
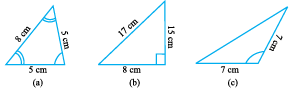
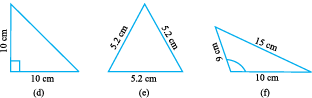
Using a protractor and a ruler find the measures of the sides and angles of the given triangles. Fill the measures in the given table.
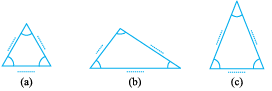
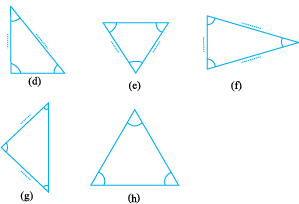
Observe the angles and the triangles as well as the measures of the sides carefully. Is there anything special about them?
What do you find?
• Triangles in which all the angles are equal.
If all the angles in a triangle are equal, then its sides are also ..............
• Triangles in which all the three sides are equal.
If all the sides in a triangle are equal, then its angles are............. .
• Triangle which have two equal angles and two equal sides.
If two sides of a triangle are equal, it has .............. equal angles. and if two angles of a triangle are equal, it has ................ equal sides.
• Triangles in which no two sides are equal.
If none of the angles of a triangle are equal then none of the sides are equal. If the three sides of a triangle are unequal then, the three angles are also............. .
Take some more triangles and verify these. For this we will again have to measure all the sides and angles of the triangles.
The triangles have been divided into categories and given special names. Let us see what they are.
Naming triangles based on sides
A triangle having all three unequal sides is called a Scalene Triangle[(c), (e)].
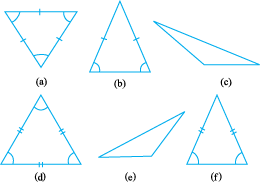
A triangle having two equal sides is called an Isosceles Triangle [(b), (f)].
A triangle having three equal sides is called an Equilateral Triangle[(a), (d)].
Classify all the triangles whose sides you measured earlier,using these definitions.
Naming triangles based on angles
If each angle is less than 90°, then the triangle is called an acute angled triangle.
If any one angle is a right anglethen the triangle is called a right angled triangle.
If any one angle is greater than 90°, then the triangle is called an obtuse angled triangle.

Name the triangles whose angles were measured earlier according to these three categories. How manywere right angled triangles?
(a) a scalene acute angled triangle.
(b) an obtuse angled isosceles triangle.
(c) a right angled isosceles triangle.
(d) a scalene right angled triangle.
Do you think it is possible to sketch
(a) an obtuse angled equilateral triangle ?
(b) a right angled equilateral triangle ?
(c) a triangle with two right angles?
Think, discuss and write your conclusions.
Exercise 5.6
1. Name the types of following triangles :
(a) Triangle with lengths of sides 7 cm, 8 cm and 9 cm.
(b) ΔABC with AB = 8.7 cm, AC = 7 cm and BC = 6 cm.
(c) ΔPQR such that PQ = QR = PR = 5 cm.
(d) ΔDEF with m∠D= 90°
(e) ΔXYZ with m∠Y = 90° and XY = YZ.
(f) ΔLMN with m∠L = 30°, m∠M = 70° and m∠N = 80°.
2. Match the following :
Measures of Triangle Type of Triangle
(i) 3 sides of equal length (a) Scalene
(ii) 2 sides of equal length (b) Isosceles right angled
(iii) All sides are of different length (c) Obtuse angled
(iv) 3 acute angles (d) Right angled
(v) 1 right angle (e) Equilateral
(vi) 1 obtuse angle (f) Acute angled
(vii) 1 right angle with two sides of equal length (g) Isosceles
3. Name each of the following triangles in two different ways: (you may judge the nature of the angle by observation)
4. Try to construct trianglesusing match sticks. Some are shown here. Can you make a triangle with
(a) 3 matchsticks?
(b) 4 matchsticks?
(c) 5 matchsticks?
(d) 6 matchsticks?
5.8 Quadrilaterals
A quadrilateral, if you remember, is a polygon which has four sides.
![]()
1. Place a pair of unequal sticks such that they have their end points joined at one end. Now place another such pair meeting the free ends of the first pair.

What is the figure enclosed?
It is a quadrilateral, like the one you see here.
The sides of the quadrilateral are AB , BC, ___, ___.
There are 4 angles for this quadrilateral.
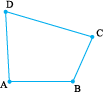
They are given by ∠BAD , ∠ADC , ∠DCB and _____.
BD is one diagonal. What is the other?
Measure the length of the sides and the diagonals. Measure all the angles also.
2. Using four unequal sticks, as you
did in the above activity, see if you can form a quadrilateral such that
(a) all the four angles are acute.
(b) one of the angles is obtuse.
(c) one of the angles is right angled.
(d) two of the angles are obtuse.
(e) two of the angles are right angled.
(f) the diagonals are perpendicular to one another.
![]()
You have two set-squares in your instrument box. One is 30° – 60° – 90° set-square, the other is 45°– 45°– 90° set square.
You and your friend can jointly do this.
(a) Both of you will have a pair of 30°– 60°– 90° set-squares. Place them as shown in the figure.
What is the measure of each of its angles?

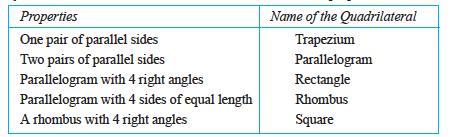
This quadrilateral is a rectangle.
One more obvious property of the rectangle youcan see is that opposite sides are of equal length.
What other properties can you find?
(b) If you use a pair of 45°– 45°–90° set-squares, you get another quadrilateral this time.
It is a square.
Are you able to see that all the sides are of equal length? What can you say about the angles and the diagonals? Try to find a few more properties of the square.
(c) If you place the pair of 30° – 60° – 90° set-squares in a different position, you get a parallelogram. Do you notice that the opposite sides are parallel?
Are the opposite sides equal?
Are the diagonals equal?
(d) If you use four 30° – 60° – 90° set-squares you get a rhombus.
(e) If you use several set-squares you can build a shape like the one given here.
Here is a quadrilateral in which a pair of two opposite sides is parallel.

It is a trapezium.
Here is an outline-summary of your possible findings. Complete it.
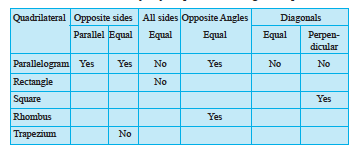
Exercise 5.7
1. Say True or False :
(a) Each angle of a rectangle is a right angle.
(b) The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length.
(c) The diagonals of a square are perpendicular to one another.
(d) All the sides of a rhombus are of equal length.
(e) All the sides of a parallelogram are of equal length.
(f) The opposite sides of a trapezium are parallel.
2. Give reasons for the following :
(a) A square can be thought of as a special rectangle.
(b) A rectangle can be thought of as a special parallelogram.
(c) A square can be thought of as a special rhombus.
(d) Squares, rectangles, parallelograms are all quadrilaterals.
(e) Square is also a parallelogram.
3. A figure is said to be regular if its sides are equal in length and angles are equal in measure. Can you identify the regular quadrilateral?
5.9 Polygons
So far you studied polygons of 3 or 4 sides (known as triangles and quardrilaterals respectively). We now try to extend the idea of polygon to figures with more number of sides. We may classify polygons according to the number of their sides.
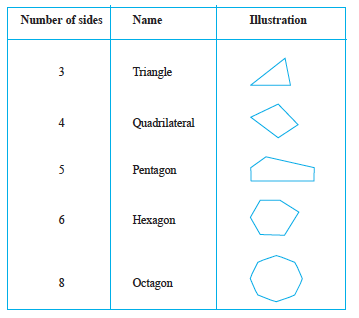
You can find many of these shapes in everyday life. Windows, doors, walls, almirahs, blackboards, notebooks are all usually rectanglular in shape. Floor tiles are rectangles. The sturdy nature of a triangle makes it the most useful shape in engineering constructions.
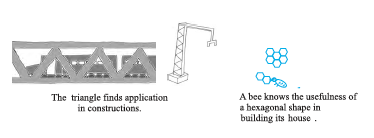
Look around and see where you can find all these shapes.
Exercise 5.8
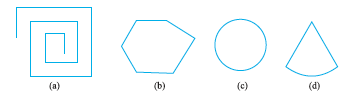
1. Examine whether the following are polygons. If any one among them is not, say why?
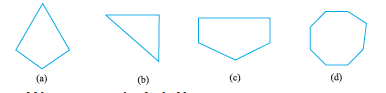
3. Draw a rough sketch of a regular hexagon. Connecting any three of its vertices, draw a triangle. Identify the type of the triangle you have drawn.
4. Draw a rough sketch of a regular octagon. (Use squared paper if you wish). Draw a rectangle by joining exactly four of the vertices of the octagon.
5. A diagonal is a line segment that joins any two vertices of the polygon and is not a side of the polygon. Draw a rough sketch of a pentagon and draw its diagonals.
5.10 Three Dimensional Shapes
Here are a few shapes you see in your day-to-day life. Each shape is a solid. It is not a‘flat’ shape.
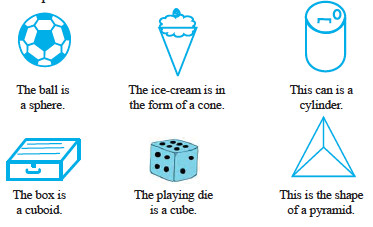
Name any five things which resemble a sphere.
Name any five things which resemble a cone.
Faces, edges and vertices
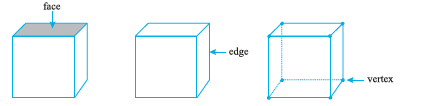
In case of many three dimensional shapes we can distinctly identify their faces, edges and vertices. What do we mean by these terms: Face, Edge and Vertex? (Note ‘Vertices’ is the plural form of ‘vertex’).
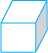
Consider a cube, for example.
Each side of the cube is a flat surface called a flat face (or simply aface). Two faces meet at a line segment called an edge. Three edges meet at a point called a vertex.
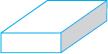
Here is a diagram of a prism.
Have you seen it in the laboratory? One of its faces is a triangle. So it is called a triangular prism.
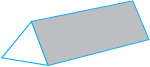 The triangular face is also known as its base.
The triangular face is also known as its base.
A prism has two identical bases; the other faces are rectangles.
If the prism has a rectangular base, it is a rectangular prism. Can you recall another name for a rectangular prism?
 A pyramid is a shape with a single base; the other faces are triangles.
A pyramid is a shape with a single base; the other faces are triangles.
Here is a square pyramid. Its base is a square. Can you imagine a triangular pyramid? Attempt a rough sketch of it.
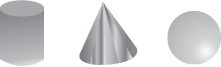
The cylinder, the cone and the sphere have no straight edges. What is the base of a cone? Is it a circle? The cylinder has two bases. What shapes are they? Of course, a sphere has no flat faces! Think about it.
![]()
1. A cuboid looks like a rectangular box. It has 6 faces. Each face has 4 edges.
Each face has 4 corners (called vertices).
2. A cube is a cuboid whose edges are all of equal length.
It has ______ faces.
Each face has ______ edges.
Each face has ______ vertices.
3. A triangular pyramid has a triangle as its base. It is also known as a tetrahedron.

Faces : _______
Edges : _______
Corners : _______
4. A square pyramid has a square as its base.
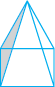
Faces : _______
Edges : _______
Corners : _______
5. A triangular prism looks like the shape of a Kaleidoscope. It has triangles as its bases.
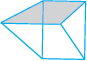
Faces : _______
Edges : _______
Corners : _______
Exercise 5.9
1. Match the following :
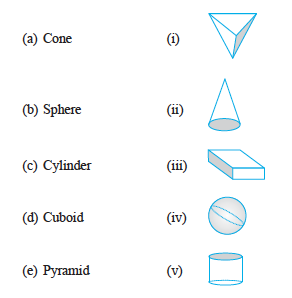
Give two new examples of each shape.
2. What shape is
(a) Your instrument box? (b) A brick?
(c) A match box? (d) A road-roller?
(e) A sweet laddu?
What have we discussed?
1. The distance between the end points of a line segment is its length.
2. A graduated ruler and the divider are useful to compare lengths of line segments.
3. When a hand of a clock moves from one position to another position we have an example for an angle.
One full turn of the hand is 1 revolution.
A right angle is ¼ revolution and a straight angle is ½ a revolution .
We use a protractor to measure the size of an angle in degrees.
The measure of a right angle is 90° and hence that of a straight angle is 180°.
An angle is acute if its measure is smaller than that of a right angle and is obtuse if its measure is greater than that of a right angle and less than a straight angle.
A reflex angle is larger than a straight angle.
4. Two intersecting lines are perpendicular if the angle between them is 90°.
5. The perpendicular bisector of a line segment is a perpendicular to the line segment that divides it into two equal parts.
6. Triangles can be classified as follows based on their angles:
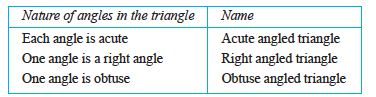
7. Triangles can be classified as follows based on the lengths of their sides:

8. Polygons are named based on their sides.
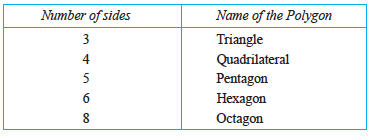
9. Quadrilaterals are further classified with reference to their properties.
10. We see around us many three dimensional shapes. Cubes, cuboids, spheres, cylinders, cones, prisms and pyramids are some of them.