Table of Contents

2
Nutrition in Animals
You have learnt in Chapter 1 that plants can prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis but animals cannot. Animals get their food from plants, either directly by eating plants or indirectly by eating animals that eat plants. Some animals eat both plants and animals. Recall that all organisms including humans require food for growth, repair and functioning of the body. Animal nutrition includes nutrient requirement, mode of intake of food and its utilisation in the body.
You have studied in Class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below:
1. ______________________
2. ______________________
3. ______________________
4. ______________________
5. ______________________
6. ______________________
The components of food such as carbohydrates are complex substances. These complex substances cannot be utilised as such. So they are broken down into simpler substances. The breakdown of complex components of food into simpler substances is called digestion.

Complex substance Simpler substances
2.1 Different ways of taking food
The mode of taking food into the body varies in different organisms. Bees and humming-birds suck the nectar of plants, infants of human and many other animals feed on mother’s milk. Snakes like the python swallow the animals they prey upon. Some aquatic animals filter tiny food particles floating nearby and feed upon them.
Activity 2.1
What is the type of food and mode of feeding of the following animals? Write down your observations in the given Table. You may find the list of modes of feeding given below the Table helpful.
Table 2.1 Various modes of feeding
| Name of animal | Kind of food | Mode of feeding |
| Snail | ||
| Ant | ||
| Eagle | ||
| Humming-bird | ||
| Lice | ||
| Mosquito | ||
| Butterfly | ||
| House fly | ||
| Ant |
(Scraping, chewing, siphoning, capturing and swallowing, sponging, sucking etc.)
| Amazing Fact |
Starfish feeds on animals covered by hard shells of calcium carbonate. After opening the shell, the starfish pops out its stomach through its mouth to eat the soft animal inside the shell. The stomach then goes back into the body and the food is slowly digested. 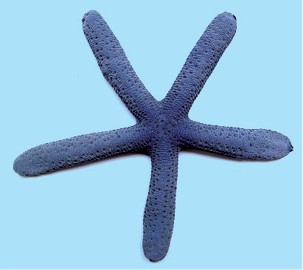 Fig. 2.1 Starfish |
2.2 Digestion in Humans
(1) the buccal cavity, (2) foodpipe or oesophagus, (3) stomach, (4) small intestine, (5) large intestine ending in the rectum and (6) the anus. Is it not a very long path? These parts together form the alimentary canal (digestive tract). The food components gradually get digested as food travels through the various compartments. The inner walls of the stomach and the small intestine, and the various glands associated with the canal such as salivary glands, the liver and the pancreas secrete digestive juices. The digestive juices convert complex substances of food into simpler ones. The digestive tract and the associated glands together constitute the digestive system.

The mouth and buccal cavity
| Milk teeth and permanent teeth |
| Do you remember about falling of your teeth some years ago? The first set of teeth grows during infancy and they fall off at the age between six to eight years. These are termed milk teeth. The second set that replaces them are the permanent teeth. The permanent teeth may last throughout life or fall off during old age or due to some dental disease. |

Activity 2.2
Wash your hands. Look into the mirror and count your teeth. Use your index finger to feel the teeth. How many kinds of teeth could you find? Take a piece of an apple or bread and eat it. Which teeth do you use for biting and cutting, and which ones for piercing and tearing? Also find out the ones that are used for chewing and grinding?


Our mouth has the salivary glands which secrete saliva. Do you know the action of saliva on food? Let us find out.
Activity 2.3
Take two test tubes. Label them ‘A’ and ‘B’. In test tube ‘A’ put one teaspoonful of boiled rice; in test tube ‘B’ keep one teaspoonful of boiled rice after chewing it for 3 to 5 minutes. Add 3–4 mL of water in both the test tubes (Fig. 2.4). Now pour 2–3 drops of iodine solution in each test tube and observe. Why is there a change in colour in the test tubes? Discuss the results with your classmates and your teacher. The saliva breaks down the starch into sugars.

Fig. 2.4 Effect of saliva on starch
The tongue is a fleshy muscular organ attached at the back to the floor of the buccal cavity. It is free at the front and can be moved in all directions. Do you know the functions of the tongue? We use our tongue for talking. Besides, it mixes saliva with the food during chewing and helps in swallowing food. We also taste food with our tongue. It has taste buds that detect different tastes of food. We can find out the position of taste buds by the following activity.
| Sweets and tooth decay |
Normally bacteria are present in our mouth but they are not harmful to us. However, if we do not clean our teeth and mouth after eating, many harmful bacteria also begin to live and grow in it. These bacteria break down the sugars present from the leftover food and release acids (see Chapter 5 to know what an acid is). The acids gradually damage the teeth (Fig. 2.5). This is called tooth decay. If it is not treated in time, it causes severe toothache and in extreme cases results in tooth loss. Chocolates, sweets, soft drinks and other sugar products are the major culprits of tooth decay. Therefore, one should clean the teeth with a brush or datun and dental floss (a special strong thread which is moved between two teeth to take out trapped food particles) at least twice a day and rinse the mouth after every meal. Also, one should not put dirty fingers or any unwashed object in the mouth. a)  b) b) c) c)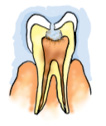 d) d)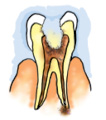 Fig. 2.5 Gradual decay of tooth Sometimes when you eat in a hurry, talk or laugh while eating, you may cough, get hiccups or a choking sensation. This happens when food particles enter the windpipe. The windpipe carries air from the nostrils to the lungs. It runs adjacent to the foodpipe. But inside the throat, air and food share a common passage. Then how is food prevented from entering the windpipe? During the act of swallowing a flap-like valve closes the passage of the windpipe and guides the food into the foodpipe. If, by chance, food particles enter the windpipe, we feel choked, get hiccups or cough. |

Activity 2.4
1. Prepare a separate sample each of
(i) sugar solution, (ii) common salt solution, (iii) lemon juice and (iv) juice of crushed neem leaf or bitter gourd.
2. Blindfold one of your classmates and ask her/him to take out the tongue and keep it in straight and flat position.
3. Use a clean toothpick to put the above samples one by one on different areas of the tongue as shown in Fig. 2.6. Use a new toothpick for each sample.
4. Ask the classmate which areas of the tongue could detect the sweet, salty, sour and bitter substances.
5. Now write down your observations and label Fig. 2.6.
Repeat this activity with other classmates.
The foodpipe/oesophagus
The swallowed food passes into the foodpipe or oesophagus. Look at Fig. 2.2. The foodpipe runs along the neck
and the chest. Food is pushed down by movement of the wall of the foodpipe. Actually this movement takes place throughout the alimentary canal and pushes the food downwards (Fig. 2.7). At times the food is not accepted by our stomach and is vomited out. Recall the instances when you vomited after eating and think of the reason for it. Discuss with your parents and teacher.


The stomach
The stomach is a thick-walled bag. Its shape is like a flattened J and it is the widest part of the alimentary canal. It receives food from the food pipe at one end and opens into the small intestine at the other.
The inner lining of the stomach secretes mucous, hydrochloric acid and digestive juices. The mucous protects the lining of the stomach. The acid kills many bacteria that enter along with the food and makes the medium in the stomach acidic and helps the digestive juices to act. The digestive juices break down the proteins into simpler substances.
The small intestine
The small intestine is highly coiled and is about 7.5 metres long. It receives secretions from the liver and the pancreas. Besides, its wall also secretes juices.
The liver is a reddish brown gland situated in the upper part of the abdomen on the right side. It is the largest gland in the body. It secretes bile juice that is stored in a sac called the gall bladder (Fig. 2.2). The bile plays an important role in the digestion of fats.
The working of the stomach was discovered by a strange accident. In 1822, a man named Alexis St. Martin was badly hit by a shot gun. The bullet had seriously damaged the chest wall and made a hole in his stomach. He was brought to an American army doctor William Beaumont. The doctor saved the patient but he could not close the hole properly and left it bandaged (Fig. 2.8). Beaumont took it as a great opportunity to see the inside of the stomach through the hole. He made some wonderful observations. Beaumont found that the stomach was churning food. Its wall secreted a fluid which could digest the food. He also observed that the end of the stomach opens into the intestine only after the digestion of the food inside the stomach is completed.
Fig. 2.8 Alexis St. Martin’s shotgun wound |
Absorption in the small intestine
The digested food can now pass into the blood vessels in the wall of the intestine. This process is called absorption. The inner walls of the small intestine have thousands of finger-like outgrowths. These are called villi (singular villus). Can you guess what the role of villi could be in the intestine? The villi increase the surface area for absorption of the digested food. Each villus has a network of thin and small blood vessels close to its surface. The surface of the villi absorbs the digested food materials. The absorbed substances are transported via the blood vessels to different organs of the body where they are used to build complex substances such as the proteins required by the body. This is called assimilation. In the cells, glucose breaks down with the help of oxygen into carbon dioxide and water, and energy is released. The food that remains undigested and unabsorbed enters into the large intestine.
Large intestine
The large intestine is wider and shorter than small intestine. It is about 1.5 metre in length. Its function is to absorb water and some salts from the undigested food material. The remaining waste passes into the rectum and remains there as semi-solid faeces. The faecal matter is removed through the anus from
time-to-time. This is called egestion.
2.3 Digestion in Grass-eating Animals
Have you observed cows, buffaloes and other grass-eating animals chewing continuously even when they are not eating? Actually, they quickly swallow the grass and store it in a part of the stomach called rumen (Fig. 2.9). Here the food gets partially digested and is called cud. But later the cud returns to the mouth in small lumps and the animal chews it. This process is called rumination and these animals are called ruminants.
| Diarrhoea |
Sometime you may have experienced the need to pass watery stool frequently. This condition is known as diarrhoea. It may be caused by an infection, food poisoning or indigestion. It is very common in India, particularly among children. Under severe conditions it can be fatal. This is because of the excessive loss of water and salts from the body. Diarrhoea should not be neglected. Even before a doctor is consulted the patient should be given plenty of boiled and cooled water with a pinch of salt and sugar dissolved in it. This is called Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS). |
The grass is rich in cellulose, a type of carbohydrate. In ruminants like cattle, deer, etc., bacteria present in rumen helps in digestion of cellulose. Many animals, including humans, cannot digest cellulose.

Animals like horses, rabbit, etc., have a large sac-like structure called Caecum between the oesophagus and the small intestine (Fig. 2.9). The cellulose of the food is digested here by the action of certain bacteria which are not present in humans.
So far you have learnt about animals which possess the digestive system. But there are many small organisms which do not have a mouth and a digestive system. Then, how do they acquire and digest food? In the section below you will learn another interesting way of food intake.
2.4 Feeding and Digestion in Amoeba
Amoeba is a microscopic single-celled organism found in pond water. Amoeba has a cell membrane, a rounded, dense nucleus and many small bubble-like vacuoles (Fig. 2.10) in its cytoplasm. Amoeba constantly changes its shape and position. It pushes out one, or more finger-like projections, called pseudopodia or false feet for movement and capture of food. Amoeba feeds on some microscopic organisms. When it senses food, it pushes out pseudopodia around the food particle and engulfs it. The food becomes trapped in a food vacuole [Fig. 2.10).

Large Intestine
Digestive juices are secreted into the food vacuole. They act on the food and break it down into simpler substances. Gradually the digested food is absorbed. The absorbed substances are used for growth, maintenance and multiplication. The undigested residue of the food is expelled outside by the vacuole.
The basic process of digestion of food and release of energy is the same in all animals. In a later chapter you will learn about the transport of food absorbed by the intestine to the various parts of the body.
| What you have learnt |
|
Exercises
- Fill in the blanks:
(b) The largest gland in the human body is __________.
(c) The stomach releases hydrochloric acid and ___________ juices which act on food.
(d) The inner wall of the small intestine has many finger-like outgrowths called _________.
(e) Amoeba digests its food in the ____________ .
(a) Digestion of starch starts in the stomach. (T/F)
(b) The tongue helps in mixing food with saliva. (T/F)
(c) The gall bladder temporarily stores bile. (T/F)
(d) The ruminants bring back swallowed grass into their mouth and chew it for some time. (T/F)
(a) Fat is completely digested in the
(i) stomach (ii) mouth (iii) small intestine (iv) large intestine
(b) Water from the undigested food is absorbed mainly in the
(i) stomach (ii) foodpipe (iii) small intestine (iv) large intestine

Extended learning — Activities and Project
(i) Why are vitamins necessary in the diet?
| S.No. | Age at which first tooth fell | Age at which last tooth fell | No. of teeth lost | No. of teeth replaced |
| 1. | ||||
| 2. | ||||
| 3. | ||||
| 4. | ||||
| 5. |
| Did you know? |
| Fats in goat’s milk are much simpler than those in cow’s milk. Therefore, the goat’s milk is much easier to digest than the cow’s milk. |